
Since the 1970s the importance of economics in international relations has increased and the study of international political ‘ economy has received increased attention. As a result, scholars focused on the relative military strength of one nation compared to others, alliances and diplomacy between nations, and the strategies nations used to protect their territories and further their own interests. Scholars believed a nation’s military power was the most important characteristic in determining how that nation would relate to others. Until the 1970s the study of international, relations centered mainly on international security studies i.e.

The Congress of Vienna, as this conference became known, was a major event in the history of international relations. But recent changes in technology and international norms have caused some scholars to question whether this system will continue in the future, or be replaced by some other system of relationships that is not yet known.įrom September 1814 to June 1815 representatives of the major European powers convened in Vienna, Austria, to reorganize Europe following the defeat of French emperor Napoleon I. The interstate system has existed for less than 500 years and is based on a common understanding of what a nation is and how it should treat other nations. They call this system the interstate system. To understand these interactions, experts look at the world as a system of nations whose actions are guided by a well-defined set of rules. Despite all of these other influences, the primary focus of international relations is on the interactions between nations. They are also affected by domestic political events and nonpolitical influences, including economics, geography, and culture. They are shaped by the primary participants in international relations, including national leaders, oilier politicians, and nongovernmental participants, such as private citinns, corporations, and nongovernmental organizations. These relationships are influenced by many variables. International relations is a broad and complex topic both for countries engaged in relationships with other nations, and for observers trying to understand those interactions. International relations mean interactions between nongovernmental groups, such as multinational corporations or international organizations such as the OIC or the United Nations (UN). International Relations is the study and practice of political relationships among the world’s nations, especially their governments. As a regular subject, international relations took start in the World War-I era and specially because of the second World War, Cold War between USA and USSR, disintegration of USSR, New World Order (NWO) of USA, global role of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) emergence of international organization and diplomatic relations etc. It was utilized by the Greeks and Romans in their relations. International relations are an old subject and can be traced in the old tribes. All these things are studied by international relations. Inter-states wars yielded post-war treaties, economic and friendly agreements and international organizations. Materialistic needs, religion, economic requirements, industrialization, security matters and trade etc. As an alone individual is nothing similarly, a state without other state is nothing and in the present complex life, a state without relations with other cannot survive. As a result, events in one part of the world have an immediate impact on the rest of the world., Therefore the states maintain regular relations with other states of the world.

In modern times the world has greatly shrunk as a result of scientific and technological development. In the very beginning of the civilized world the states were mutually interlinked. The number 1,000,000 has 10 digits (1,000,000 = 1 x 10^6).Meaning and Nature of International Relations It is the number of digits a number has multiplied by 10.
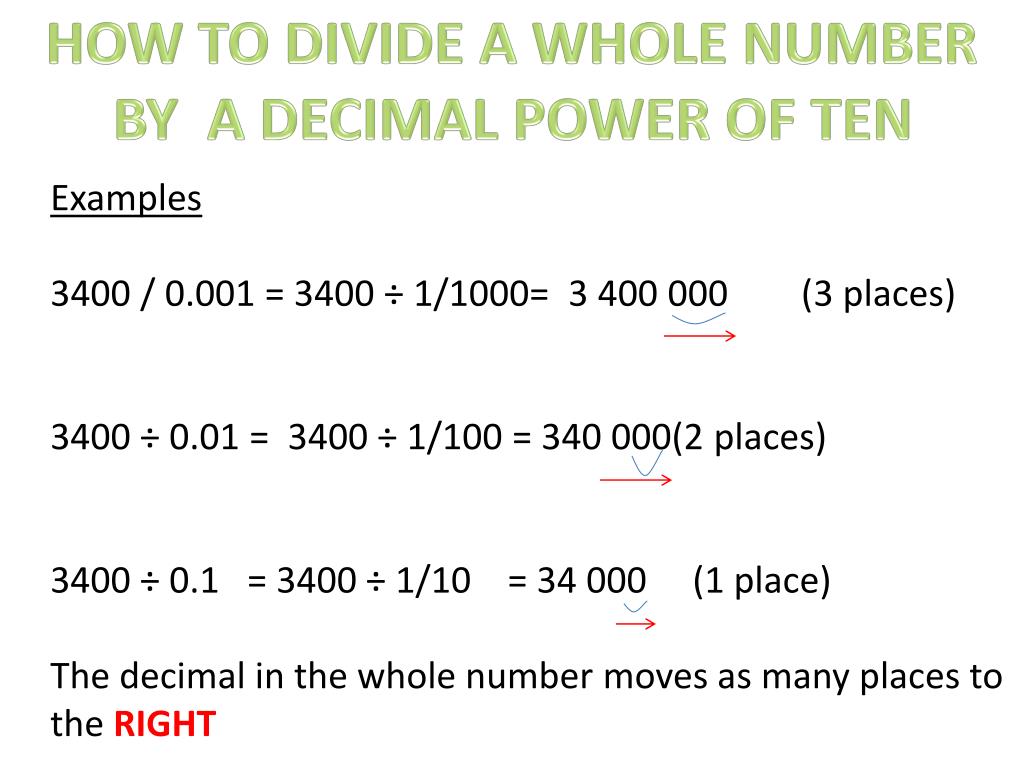
The power of 10 is a mathematical concept that helps people understand large numbers. Prefixes are used to indicate a number that is multiplied by a power of 10. To divide powers of 10, subtract the exponents.įor example, 10 ÷ 10 = 1, because 10 − 0 = 10 and 10 − 1 = 9. To multiply powers of 10, add the exponents.įor example, 10 × 10 = 100, because 10 + 0 = 10 and 10 + 1 = 11. Powers of 10Ī power of 10 is a number that is multiplied by itself 10 times. When expressing a number in scientific notation, the number is multiplied by 10 to the power of the exponent.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
